BITMAPS or raster graphics |
VECTOR GRAPHICS |
||
Originates from the need to translate a photograph into a digital file. Photographs have continuous tone and color change that is captured as a very "tight mosaic" of tini tassels, one of each solid color, called pixels; producing a grid or "map of bits". |
Graphics created in a digital format, their content is saved as a mathematical formula. |
||
 Bitmaps tend to compress better as jpegs, because of the continuous tone-change implied in their photographic nature. Bitmaps tend to compress better as jpegs, because of the continuous tone-change implied in their photographic nature. |
 Vector-based images tend to compress better as gifs, because of their strong outlines and areas of flat colors. Vector-based images tend to compress better as gifs, because of their strong outlines and areas of flat colors. |
||
Bitmaps are resolution Dependent because the data describing the image (the amount of pixels) is fixed to a grid of a particular size. Your file has a certain printing size and it cannot be increased. You can scale it down, by "throwing away some of the pixels" but if you try to increase the amount of pixels, the result will loose detail and look blurred because of the bitmap program (photoshop) trying to fix the broblem of lack of original pixels. |
Vector graphics are resolution Independent: they can be displayed on output devices of varying resolutions without loosing quality. When you export a vector based file into a bitmap one (ex:Illustrator to Photoshop)you can freely choose the size the canvas will have when exported to bitmap because vector -based graphics scale big or small without loosing any quality. |
||
| The content of a bitmap file looks good when seen at 100% scale, but if you zoom in beyond its total size you will begin to see the grid of pixels, each pixel made of one solid color. | Moving, resizing, reshaping or changing the color of a vector-graphic shape/s doesn't change the quality of it's appearance on screen or printed. | ||
An image of certain dimmensions will need acorrespondent amount of pixels to provide detail and content to it. |
Beware of methods like Live-trace in Illustrator or Trace-bitmap in Flash that can potentially create hundred of thousands of polygons. |
||
| Bitmaps are measured by the amount of pixels per inch (ppi). When we are referring to printing resolution, we can also talk about the number of dots per linear inch (dpi). The numeric value is the same in both cases, anyway. The higher the resolution, the bigger the image, because it is using more pixels for it's representation. |
|||
 |
|||
| Above this, you can see an image at its full resolution, at 100% scale. The image is 333 X 223 pixels big. | |||
| On the right, I have taken at snapshot at a detail of the same image (the base of the glass) zoomed in and I have saved it for you. You can distinguish the pixels that form the base, the napkin and the dot. There are many different shades of color configuring simple elements.Each square is filled with ONE only tone. Pay attention at round edges of objects. This is typical of bitmaps with a high resolution: you need a lot of different color squares to solve a soft-round edge. Because the basic grid is square based you have to work like in a "staircase" to produce a curve. This effect of smoothing the tones of pixels at the edge of a curve is called Antialiasing and it is very important when rasterizing Type. |
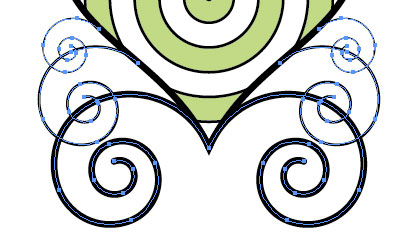
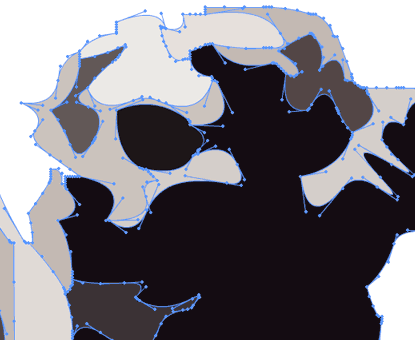
Vector based images are constructed with points, that create paths. Any given point has a position, referencing the right-left corner of the image, so the whole image can be described as a simple list of numbers. |
  |
||
| It is important to talk about a certain type of point called "Bezier point". This is the secret behind the flexibility and accuracy of vector graphics' rendering. Bezier points store, besides position, tension to the next and previous point (represented by the angle and distance of the "anthenas" or direction handles). This makes possible all types of beautifully rendered curves with very few points. |
|||
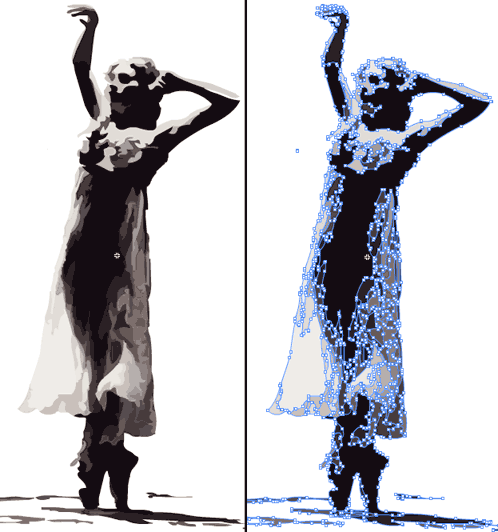 |
 |
||
The images above are snapshots of artwork rendered in Flash. Adobe Flash is probably the best 2D animation program currently available. |
|||
 |
||
The image above is displayed at its full resolution. |
||
 |
||
Here you can see the same low-res image expanded to 500 X 350 pixels. On the right you can see the same photograph with a higher resolution. |
||

The pixel resolution of DIGITAL VIDEO on screen is 640 X 480 pixels.
Digital video use to have a 4:3 aspect ratio.
The new HD formats have a 16:9 aspect ratio, commonly known as wide screen.
Half screen is 320 X 240 pixels (used on web-video).
Mp3 as a compressed audio format.
 The more pixels, the bigger file size.
The more pixels, the bigger file size. File size is related to the amount of polygons, not to the dimmenison of the image.
File size is related to the amount of polygons, not to the dimmenison of the image.